"Maximizing Efficiency: How Material Requirements Planning (MRP) in SAP Can Streamline Your Manufacturing Process"
- Harwinder Singh
- Mar 29, 2024
- 4 min read
Updated: Apr 2, 2024

In the world of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, SAP stands out as one of the most widely used platforms for managing various aspects of business operations. Among its many modules, Material Requirements Planning (MRP) plays a crucial role in streamlining inventory management and production processes. In this blog post, we'll delve into the fundamentals of MRP in SAP, its key features, and its significance in optimizing supply chain operations.
What is Material Requirements Planning (MRP)?
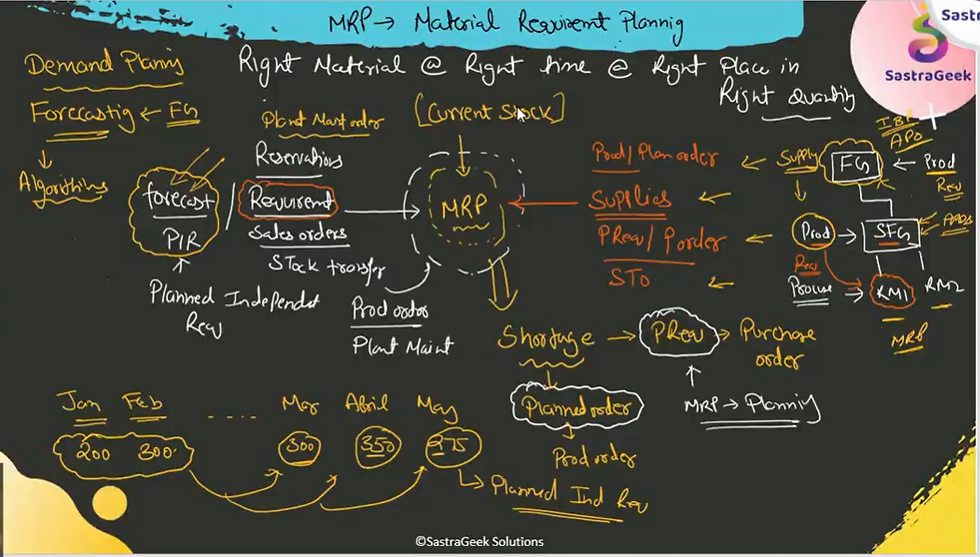
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a method used to plan and control the inventory levels and production schedules of finished goods, subassemblies, and components within a manufacturing or production environment. It ensures that materials are available for production and that products are available for delivery to customers when needed while minimizing inventory carrying costs.
The Role of MRP in SAP
Within the SAP ecosystem, MRP is facilitated through the Materials Management (MM) module. MRP in SAP helps businesses effectively manage their material resources by providing insights into demand, inventory levels, and production schedules. Here's how MRP operates within SAP:
Demand Forecasting: MRP in SAP starts with forecasting demand based on sales orders, production plans, and historical data. By analyzing these inputs, SAP calculates the quantity and timing of materials needed for production.
Bill of Materials (BOM) Management: A crucial aspect of MRP is managing the Bill of Materials, which lists all the components and raw materials required to manufacture a product. SAP allows businesses to create and maintain BOMs, which are then used by the system to generate procurement proposals.
Inventory Management: MRP in SAP helps optimize inventory levels by ensuring that materials are neither overstocked nor understocked. It considers factors such as lead times, safety stock levels, and reorder points to calculate the optimal inventory levels.
Production Planning and Scheduling: Based on demand forecasts and BOMs, SAP MRP generates production plans and schedules, ensuring that manufacturing processes are aligned with customer demands. It helps in optimizing production resources and minimizing idle time.
Procurement and Purchasing: MRP in SAP generates procurement proposals for purchasing raw materials and components based on demand forecasts and inventory levels. These proposals can be converted into purchase orders, facilitating the procurement process.
MRP types in SAP
There are different algorithms, known as MRP types, available in MRP:
PD and VB are commonly used MRP types.
PD is based on demand requirements from higher levels and suggests shortage solutions.
VB is reorder-based planning, where the system generates purchase requisitions when stock levels drop below reorder points.
M0 is for master scheduling runs, generally used for finished and critical materials planning.
MRP areas
MRP areas are organizational structures where MRP can be executed independently. MRP areas can be defined within a plant and can include one or more storage locations. MRP areas are planned separately, and MRP-relevant material master data is maintained for each MRP area independently.
MRP groups
MRP groups are objects that contain all the materials from the point of view of MRP. MRP groups are used when the plant division for planning is not enough for the division of the different materials MRP requirements. MRP groups are maintained on the plant level and are a means of controlling how a material is planned if it does not to follow the generic plant planning parameter settings.

Key Features of MRP in SAP
Master Data Management: SAP MRP relies on accurate master data, including material master records, BOMs, and work center data, to perform its calculations effectively.
Planning Parameters: Businesses can customize planning parameters in SAP MRP to suit their specific requirements, such as lead times, safety stock levels, and lot sizes.
Simulation Capabilities: SAP MRP offers simulation features that allow businesses to simulate different scenarios and evaluate the impact on production schedules, inventory levels, and resource utilization.
Integration with Other SAP Modules: MRP in SAP seamlessly integrates with other modules such as Sales and Distribution (SD), Production Planning (PP), and Financial Accounting (FI), ensuring data consistency across the organization.

Benefits of MRP in SAP
Improved Efficiency: By automating the planning and scheduling processes, SAP MRP improves efficiency and reduces the time and effort required for manual planning.
Optimized Inventory Levels: MRP helps businesses maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing carrying costs while ensuring that materials are available when needed.
Enhanced Customer Service: By aligning production with demand, SAP MRP enables businesses to fulfil customer orders on time, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
Cost Savings: Through better inventory management and resource utilization, SAP MRP helps businesses minimize wastage and reduce operational costs.
Master data creation
Create a material in SAP by following the steps below:
Goto MM01 transaction code - material master creation
Enter the material number
Select the industry sector and material type
Select the views- basic data 1, purchasing, MRP 1 2 3 and accounting 1 view (Views maintained as per the business needs)
Enter the Org Levels - Plant and Storage Location
Basic data 1 - enter a description, the base unit of measure and the material group
Purchasing - Description, Basic Unit of measure, Material Group, GR processing time
MRP 1 - MRP Type as PD, MRP Controller, Lot Sizing Procedure as MB, Minimum Lot Size, Maximum Lot Size.
MRP 2 -Storage Location, Planned Delivery time, Safety stock
MRP 3 -Strategy group as 10- Make to Stock, Availability check 02- Individual requirements
Accounting -Valuation class, standard price, price control V for moving average (mostly for raw material) and S standard (For FG products) and Save it By completing these steps, the material with MRP-type PD was successfully created in SAP.
In conclusion, Material Requirements Planning (MRP) in SAP is a powerful tool for optimizing inventory management, production planning, and procurement processes within manufacturing and production environments. By leveraging the capabilities of SAP MRP, businesses can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction, ultimately gaining a competitive edge in today's dynamic market landscape.
Harwinder Singh
SAP MM/EWM Consultant
§ LinkedIn profile
§ SAP Blogs
Follow me on LinkedIn.
I am a content creator who shares knowledge through the content I create. I have top SAP Gurus and Expert Connections over there who share their knowledge, talk about the latest technology, and much more.











Thanks for the tips, very useful. Appreciate your effort. certified translation services miami
This is exactly what I needed to read. Thanks for the motivation. certified translation los angeles
Los vinilos decorativos son una solución práctica, versátil y elegante para transformar cualquier espacio. Ideales para hogares, oficinas, comercios y espacios deportivos, permiten personalizar paredes, cristales, baños, muebles y zonas especiales sin necesidad de reformas complicadas. Su facilidad de instalación, variedad de diseños y adaptabilidad los convierte en la opción perfecta para cualquier estilo de decoración.
Vinilos decorativos para paredes
Decorar las paredes con vinilos es una de las formas más efectivas de cambiar la estética de cualquier habitación. Los vinilos decorativos para paredes de cocina modernos grandes son ideales para cocinas amplias y modernas, combinando diseño, color y funcionalidad sin necesidad de grandes reformas. Además, el catálogo de vinilos decorativos para paredes ofrece opciones para todas las estancias, desde salones y…
bacan4d | bacan4d slot | bacan4d togel | bacan4d toto |slot gacor | bacan4d login | bacan4d review | rtp bacan4d |bacan4d maxwin | situs mudah maxwin | slot toto | toto slot | slot88 | slot gacor | slot thailand | toto4d | toto gacor
Thank you for sharing another insightful blog. Where else can I find that kind of knowledge presented in such a perfect way? I have been searching for such information because I am currently working on a project. fort lauderdale traductor